The research paper reveals the potential to further expand the extensive family of nanostructured materials. Images: From Science 2017, 358, 514-518. Reprinted with permission from AAAS.



The research paper reveals the potential to further expand the extensive family of nanostructured materials. Images: From Science 2017, 358, 514-518. Reprinted with permission from AAAS.
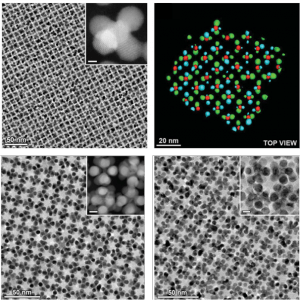
The self-assembly of inorganic nanoparticles has been used to prepare hundreds of different colloidal crystals, but almost invariably with the restriction that the particles must be densely packed. Here, we show that non-close-packed nanoparticle arrays can be fabricated through the selective removal of one of two components comprising binary nanoparticle superlattices.
First, a variety of binary nanoparticle superlattices were prepared at the liquid-air interface, including several arrangements that were previously unknown. Molecular dynamics simulations revealed the particular role of the liquid as a template for the formation of superlattices not achievable through self-assembly in bulk solution. Second, upon stabilization, all of these binary superlattices could be transformed into distinct “nanoallotropes” – nanoporous materials having the same chemical composition but differing in their nanoscale architectures.
Read more:
Udayabhaskararao T. et al.,
Science 358, 514 (2017).
Press release “Fabricatio of porous materials with novel crystal structures as sembled from nanoparticles” published on 2017-10-26 by CIC biomaGUNE.
SoftComp partners: CIC biomaGUNE/University of Antwerp